Deployment Guide
Background
ColorTokens Xshield gives you a single-pane-of-glass approach to manage micro-segmentation for all types of assets : data center servers, cloud workloads, containers, user endpoints, Internet-of-Things, Operational Technology devices, and even legacy operating system devices.
The Xshield platform employs agents or gatekeepers to enforce detailed policies for micro-segmentation. While agents necessitate deployment on each protected system, the Xshield gatekeeper seamlessly integrates into existing networks with minimal disruption. Positioned within the subnet, typically a LAN/VLAN, the gatekeeper functions as a distinct network component. It operates through two networks: an upstream network for inbound and outbound communication, and a downstream network to connect all the devices the gatekeeper is positioned to secure. Once activated within the subnet, the gatekeeper assumes the role of gateway for all the devices in your downstream network.
Deploying XShield Gatekeeper
This gatekeeper can be deployed either as a hardware or virtual gatekeeper, with both options utilizing the same Xshield gatekeeper software.
-
Hardware Gatekeeper from ColorTokens
-
Virtual Gatekeeper in ESXi or other virtualization platform using either OVA or ISO image
The difference lies in the execution environment: In the virtual gatekeeper this software runs within a virtualization environment such as VMware, while in the case of a hardware gatekeeper, this is a physical gatekeeper device.
Hardware Gatekeeper Installation (Using ISO)
The hardware gatekeeper can either be a ColorTokens Xshield gatekeeper box such as the one below or compatible hardware on amd64 architecture which can run ubuntu 22.04.

This section describes how to utilize the ISO image from the gatekeeper download page of the Xshield console to setup a hardware gatekeeper.
Note that only amd64 based hardware capable of running ubuntu linux 22.04 and having two physical ethernet ports is supported with this ISO image.
Create Bootable USB from ISO
To write the raw ISO image directly to a USB drive on Windows, you can use the media creation tool. For Linux / macOS systems, you can use a simple command line utility to write the ISO image to USB drive or use applications like balenaEtcher.
-
Determine the USB device using below command:
$ sudo lsblk -
If the USB device is /dev/sdb, then you would use below command to burn the ISO image to the drive. Note, that this assumes the ISO image is in current directory.
sudo dd bs=32M if=ctgatekeeper-base.iso of=/dev/sdb
Boot Hardware Gatekeeper from the Bootable USB
- Connect to the gatekeeper serial console (using minicom / TeraTerm / etc) or connect HDMI monitor and keyboard and power it up. Go into the boot configuration menu (typically F11) and select the USB stick as the boot device.
- Next, the bootloader will prompt you with some options. Select "Install ColorTokens Xshield Gatekeeper" from the menu and press enter.
- The Live image will boot the kernel from the USB stick and should automatically begin the process of overwriting the internal hard drive (/dev/sda).
- When the process is complete, you will be prompted to remove the USB stick and to press any key to reboot.
- Now the gatekeeper will boot from the internal HDD. Once the OS is up, login prompt will be shown indicating the Xshield gatekeeper version: 3.0.xxxx, MAC address, Machine ID.
- The default admin user is "admin". The password is "colortokens".
The admin account is configured to expire this password, so it must be changed immediately upon logging in for the first time.
Once the system is up and running, follow the procedures in the Gatekeeper Registration section below.
Virtual Gatekeeper Installation
Virtual gatekeepers can be deployed on ESXi or other virtualization platforms using either OVA or ISO image. Shown below is a sample configuration of a virtual gatekeeper running on VMware ESXi 6.5.
Using OVA Image
Prerequisites
-
ESXi 6.5 or above is required.
-
Determine the networking details for the WAN (upstream) interface.
Here is a sample networking configuration for the WAN interface. This configuration must be functional to enable communication between the gatekeeper and the Xshield platform and the same can be edited from the Xshield console.
WAN Details Example:
- Subnet: 10.1.60.0/22
- IP Address: 10.1.63.249
- Gateway IP: 10.1.60.1
- DNS Address: 10.1.3.250, 10.1.2.11
Installation Steps
-
Download OVA image for a gatekeeper from the Gatekeeper Downloads page of the Xshield Console.
-
Create a Virtual Machine (VM) out of the OVA image on ESXi server – named gatekeeper1, gatekeeper2 (you can name it as per your choice).
-
In ESXi Server check following:
-
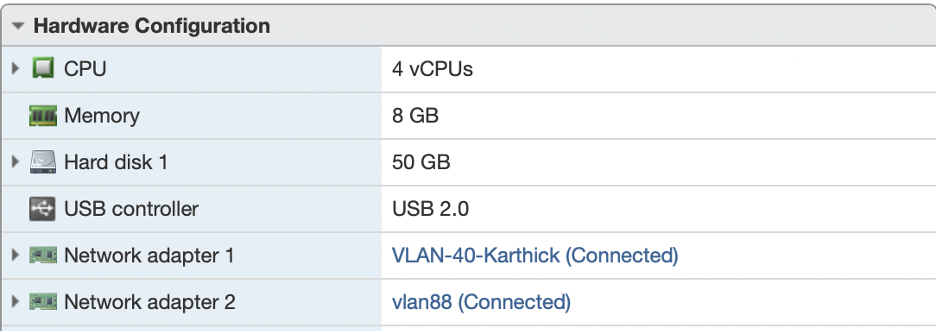
3.1. Ensure the two ports WAN (ens160) and LAN (ens192) of the Primary Gatekeeper are connected to the WAN and LAN network/virtual port group respectively. LAN corresponds to the segment which is going to be controlled by the gatekeeper.
-
3.2. Ensure the two ports WAN (ens160) and LAN (ens192) of the Standby Gatekeeper are connected to the WAN and LAN network/virtual port group respectively.
-
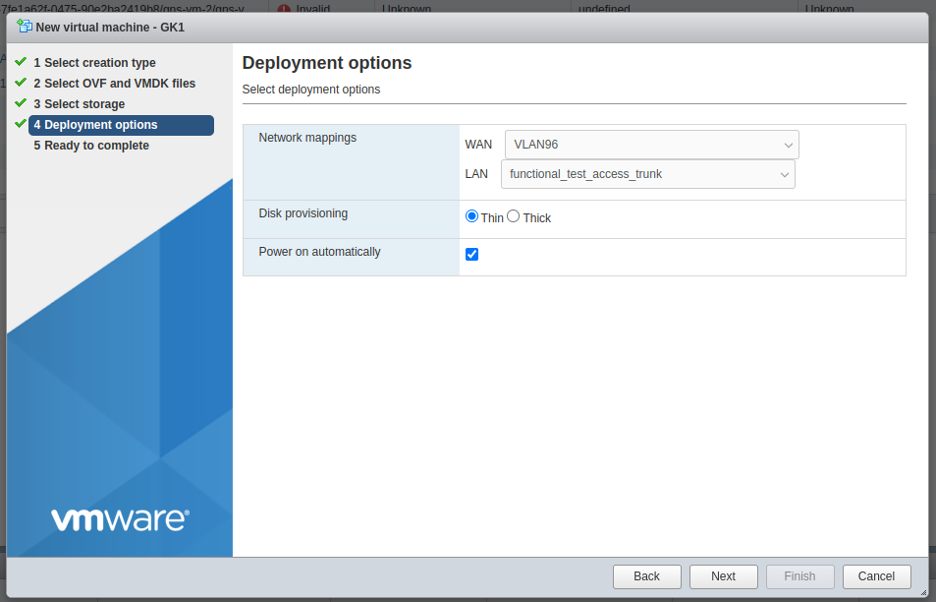
3.3. Ensure that the default VM settings such as RAM size (default 8GB), # of CPU cores (default 4), or HD size (default 40GB). Note: the file system will automatically expand to the size configured here when the image is first booted up.
-
3.4. Power ON the VM in ESXi console.
-
Increasing Disk Size and Configuring Network Interfaces
-
Select WAN and LAN virtual port groups:
-
After creating and powering on the VM which was created from OVA, the disk will be of size 4.3 GB only. User needs to increase the size by performing following steps: power off VM, edit VM setting and set the size to 50GB (as per need):
-
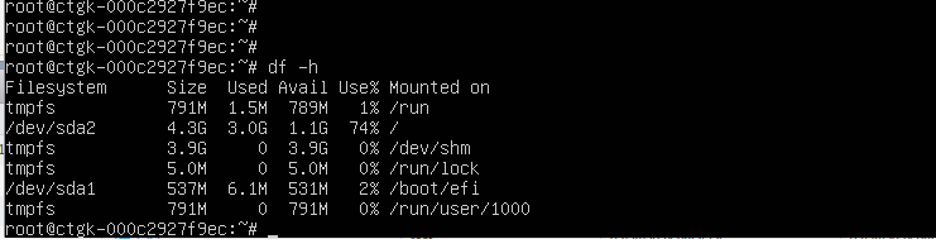
Power on and execute following from the VM console:
growpart -v /dev/sda 2 (space between /dev/sda and 2)
resize2fs /dev/sda2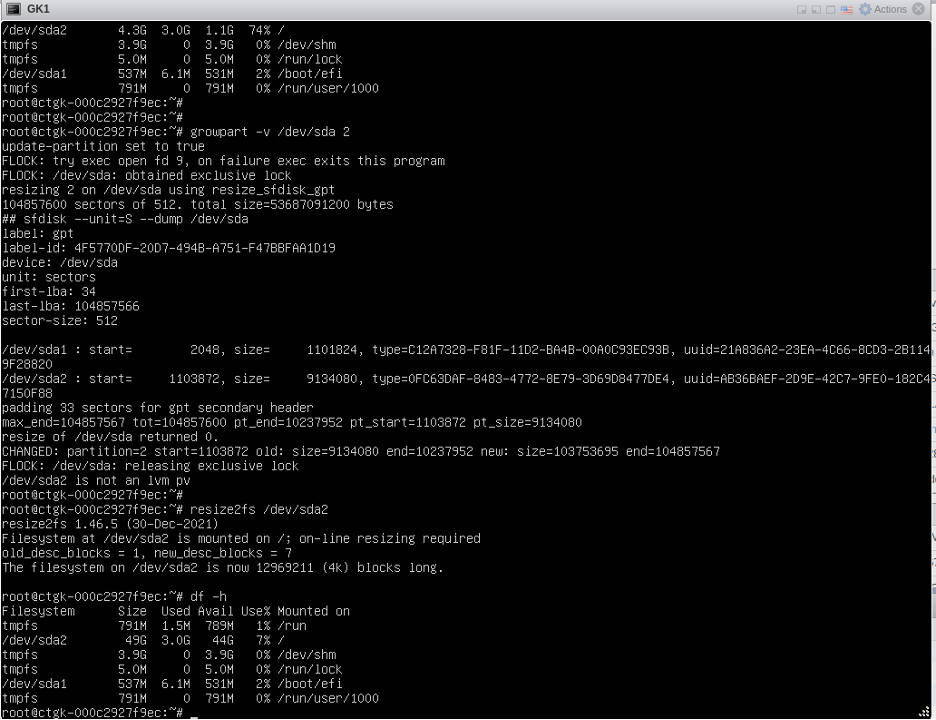
Once the system is up and running, follow the procedures in the Gatekeeper Registration section below.
Using ISO Image
ISO can be used to boot Gatekeeper VM on ESXi, VirtualBox, etc. instead of OVA based gatekeeper deployment.
Installation Steps
-
Create new VM in ESXi:
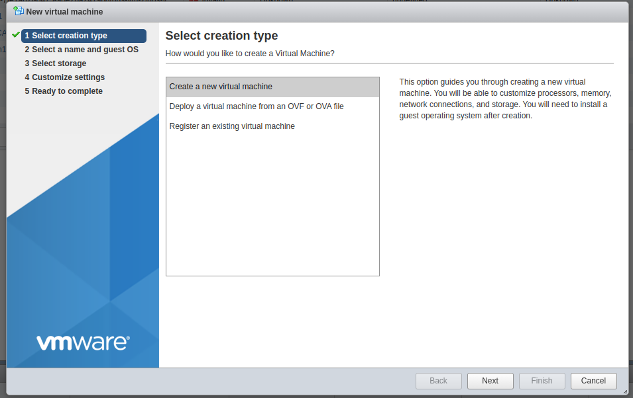
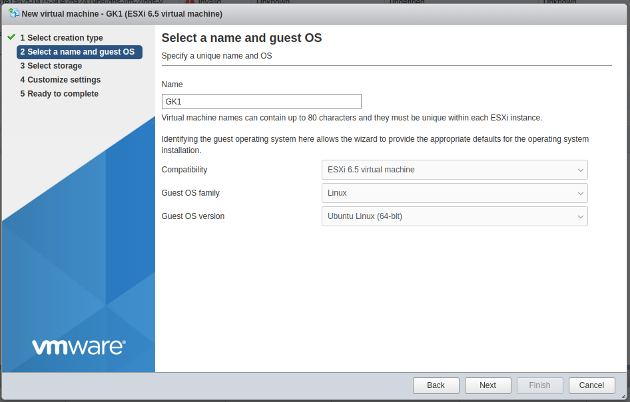
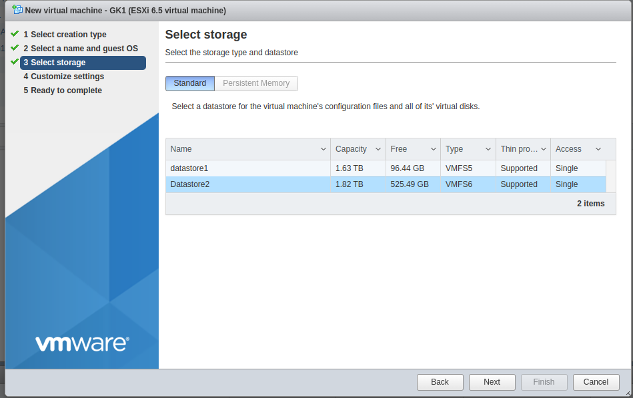
-
Select 4 CPU, 8GB RAM, 2 Network Adapters, and attach the ISO file:
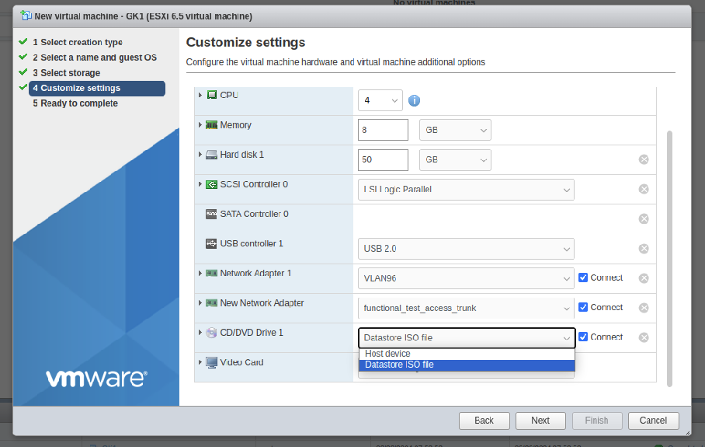
-
Finish creating the VM and power on the VM:
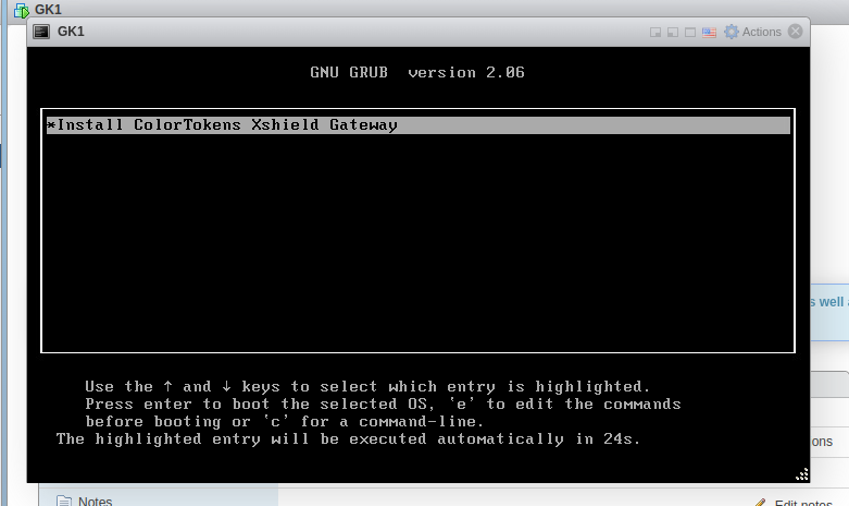
-
The bootloader will prompt you with some options. Select "Install ColorTokens Xshield Gatekeeper" from the menu and press enter.
-
The Live image will boot the kernel from the ISO and should automatically begin the process of overwriting the internal hard drive (/dev/sda).
-
When the process is complete, the VM will reboot. Once the OS is up, login prompt will be shown indicating the Xshield gatekeeper version: 3.0.xxxx, MAC address, Machine ID.
-
The default admin user is "admin". The password is "colortokens".
Note 1: If the following error is observed - "Cannot continue installation - system is not configured with UEFI boot":
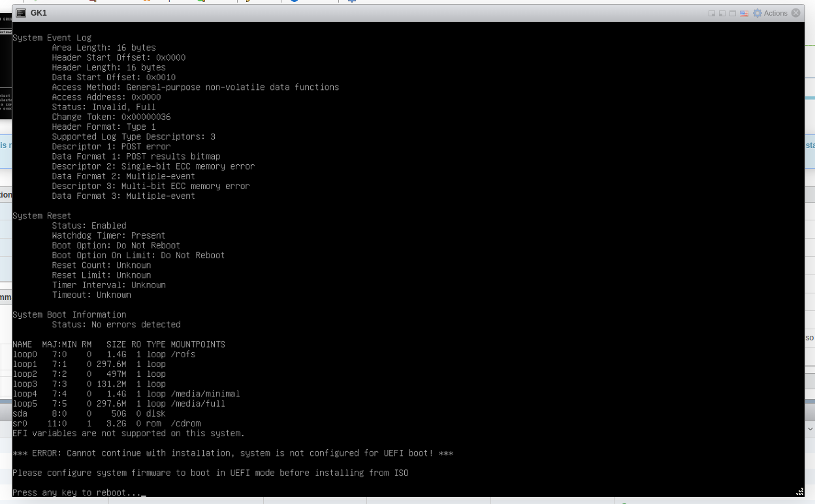
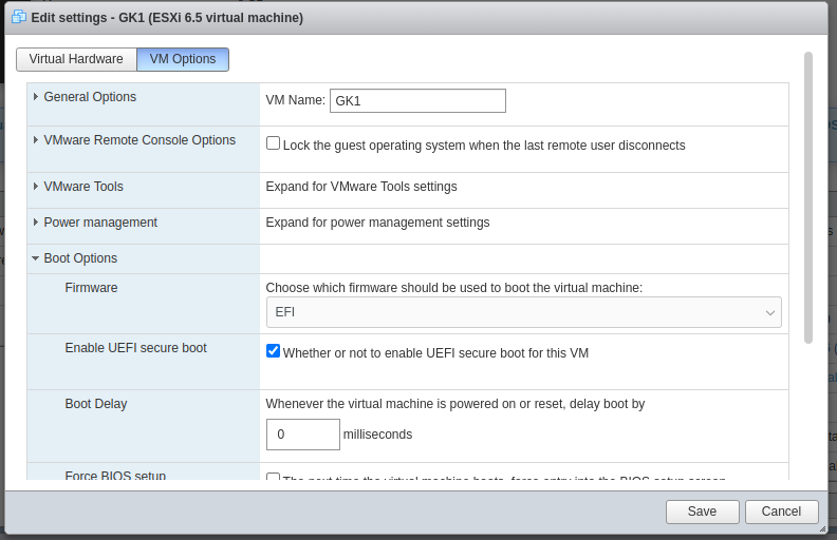
Power off the VM and set UEFI boot:
Note 2: If the installation process is not able to identify the DISK to be selected for writing, the installation process will list down the system information and indicate which disk is selected for writing. The user will be prompted to press any key to select the disk manually. User should key-in the disk name as /dev/xxx:
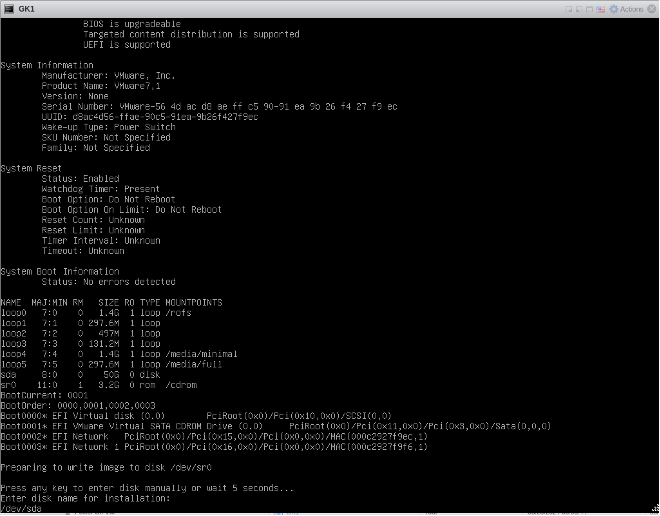
After this, installation process will start writing to the disk /dev/sda:
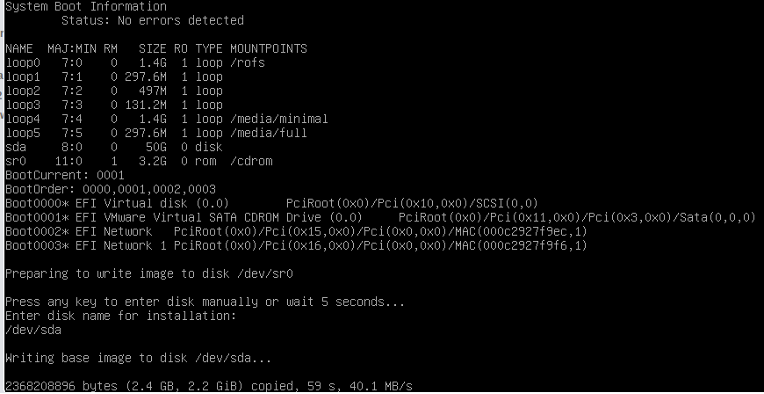
Once the system is up and running, follow the procedures in the Gatekeeper Registration section below.
Gatekeeper Registration
Initial Setup
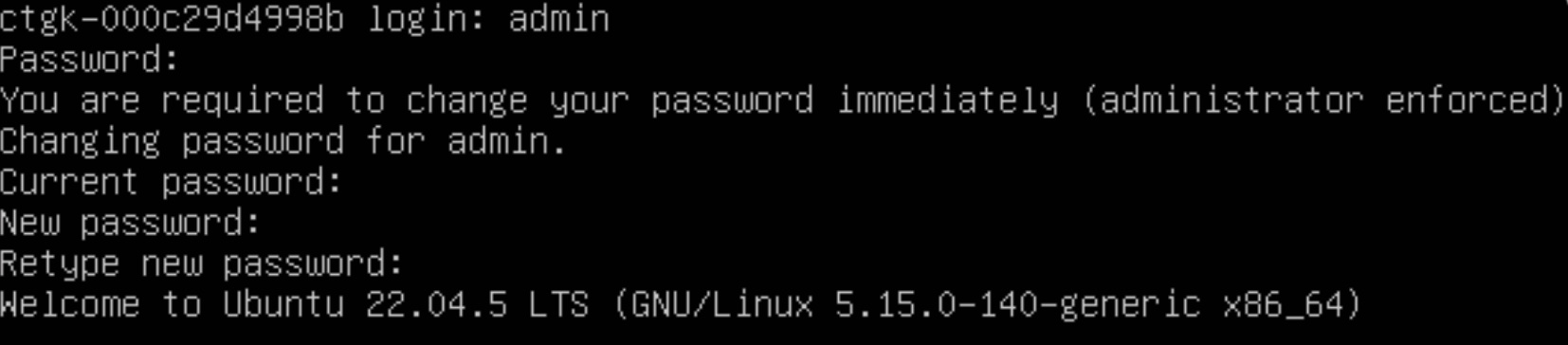
- Bootup and login: Hook up a console cable to the box and boot up the gatekeeper (hardware gatekeeper). Login to the gatekeeper to see CLI options using the username "admin" and password as "colortokens" (The same step can be done via ESXi console for virtual gatekeeper) You will then be required to enter a complex password consisting of:
- 8 or more characters
- 1 Upper case
- 1 Lower case
- A number
- A special character
-
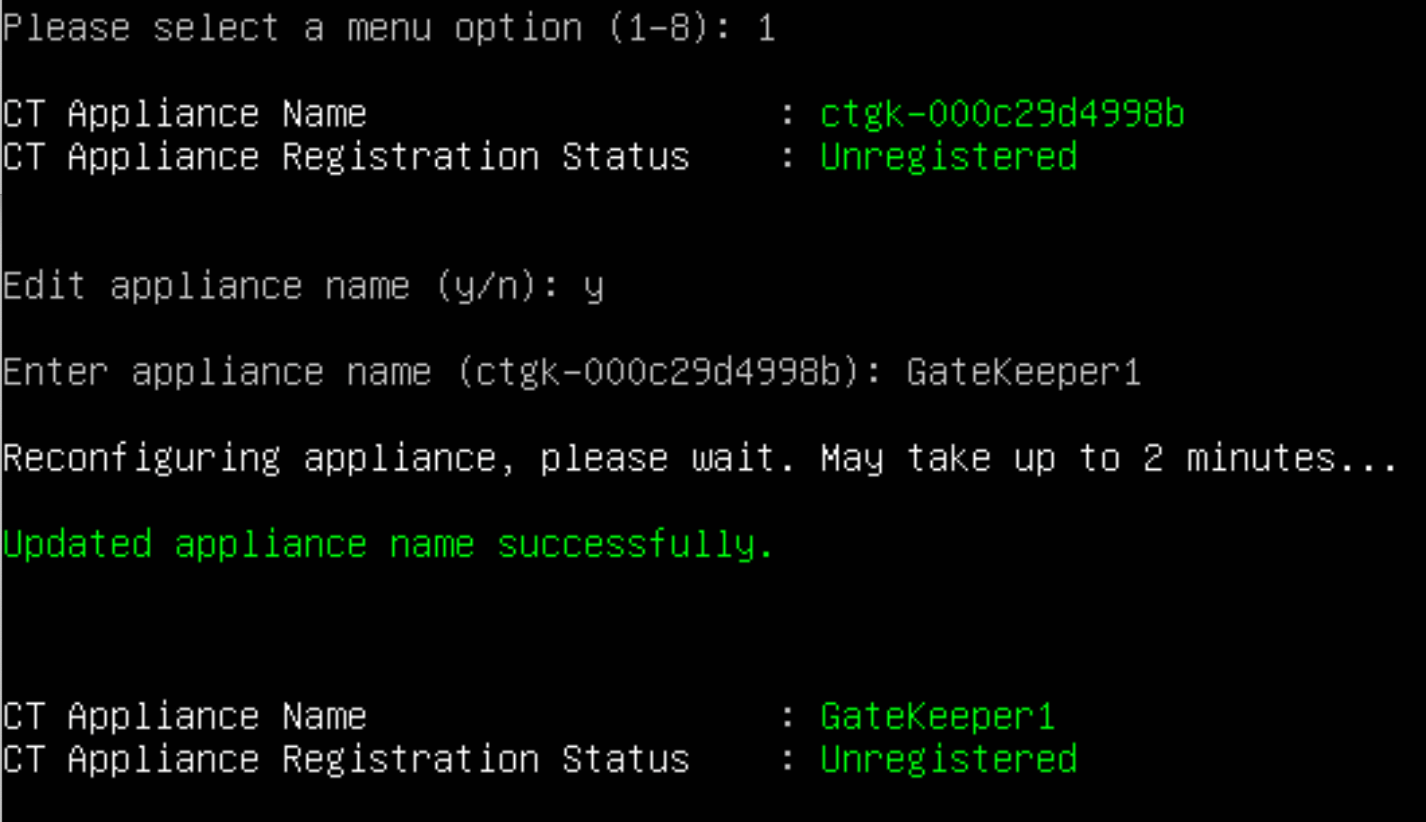
Enter gatekeeper name When you start the CLI, a default gatekeeper name appears. It is highly suggested you set a meaningful gatekeeper name. Select 1 follow the prompts and enter a name
-
Setup WAN interface Next, you will see some information about your gatekeeper. Configure the WAN or unprotected interface of the gatekeeper. This is also the interface that can reach the management platform. You need to know:
- IP address and Netmask
- Gateway Address
- DNS Server (if Saas)
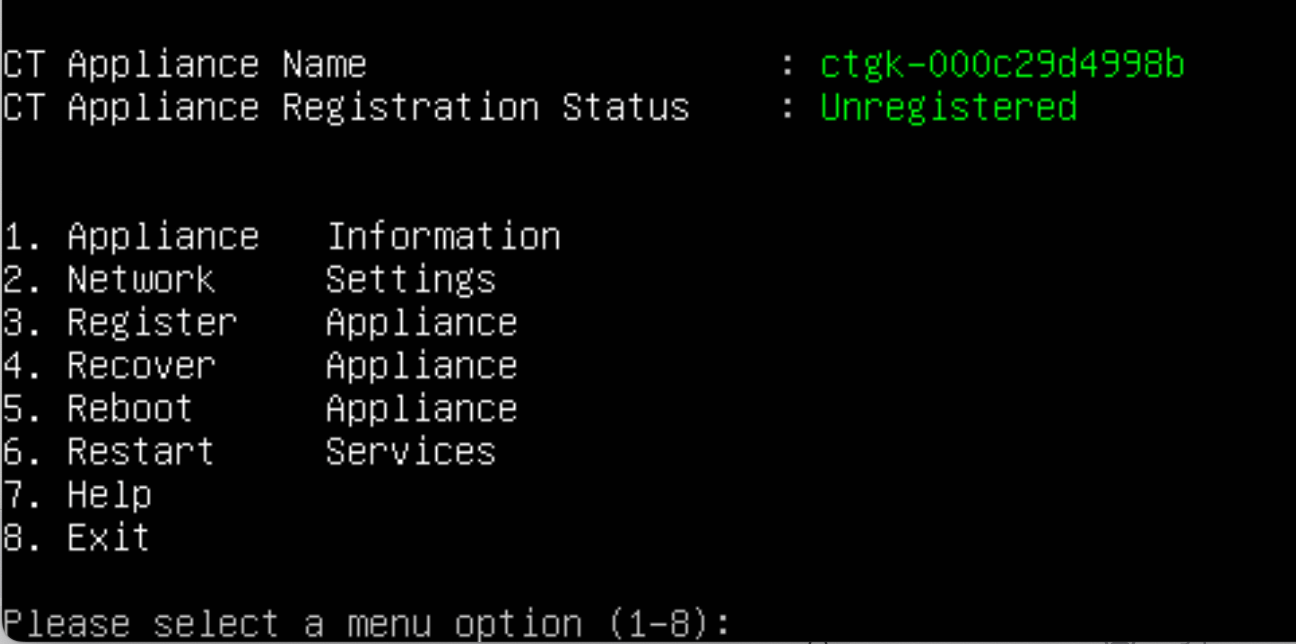
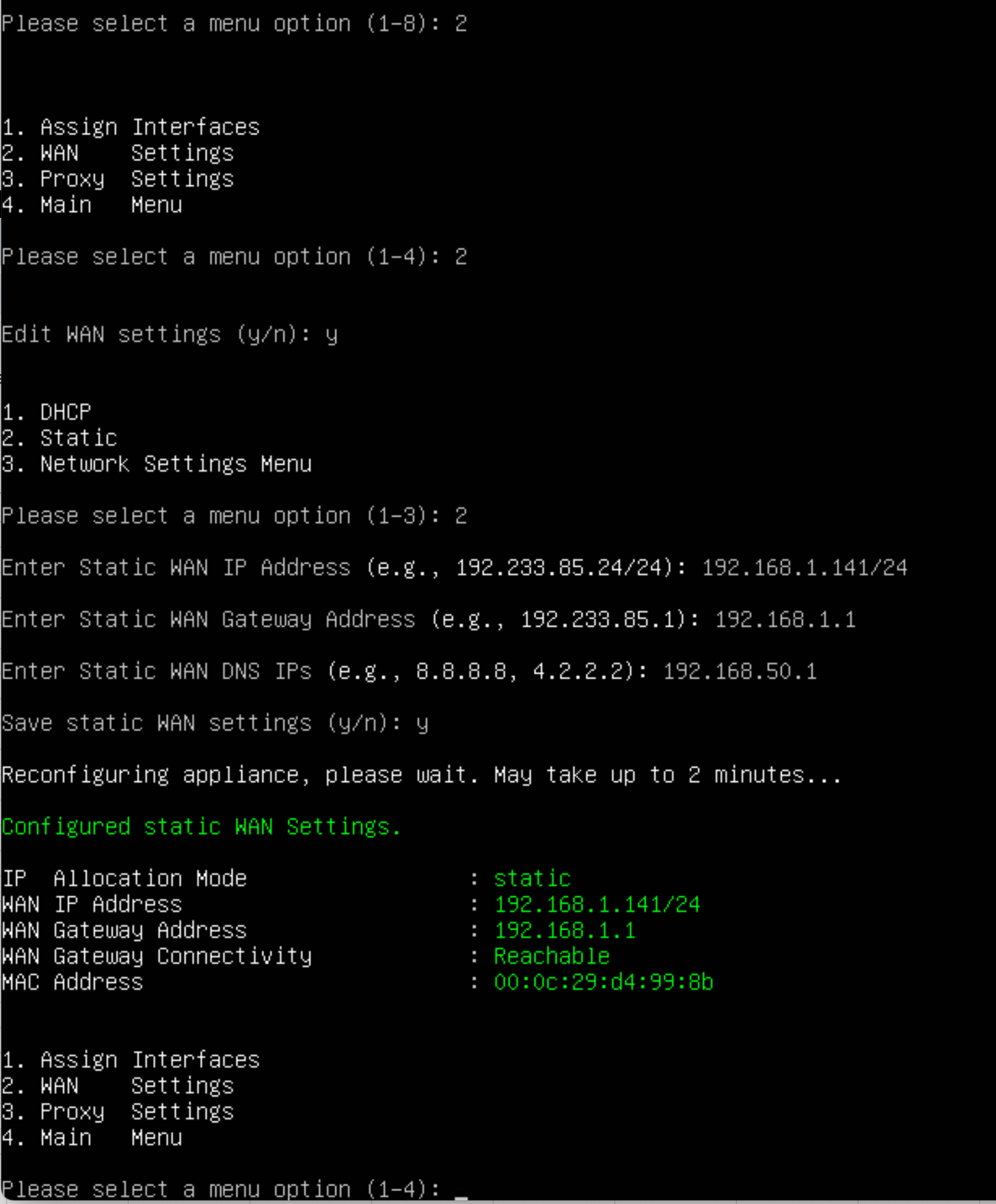
Once the gatekeeper is configured and the displayed information is correct, you can register it with the management platform. Select option 3 from the Main Menu to register the gatekeeper.
Registration Methods
There are two methods to register a gatekeeper with the Xshield console:
Method 1: Register with Activation Code
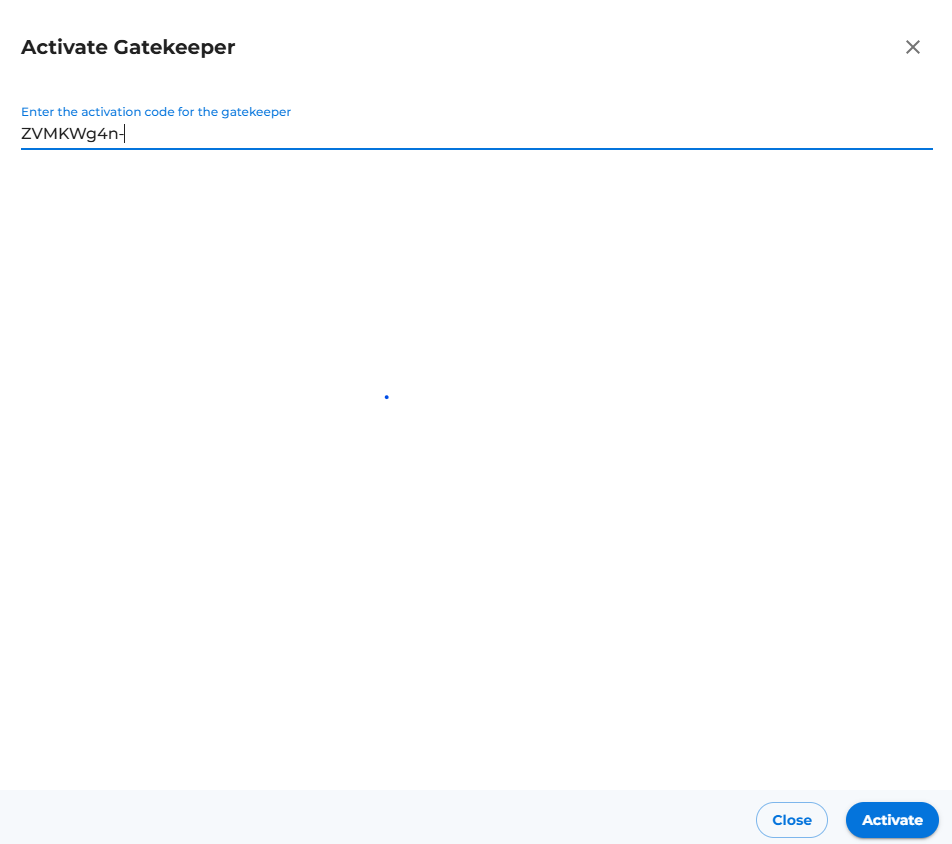
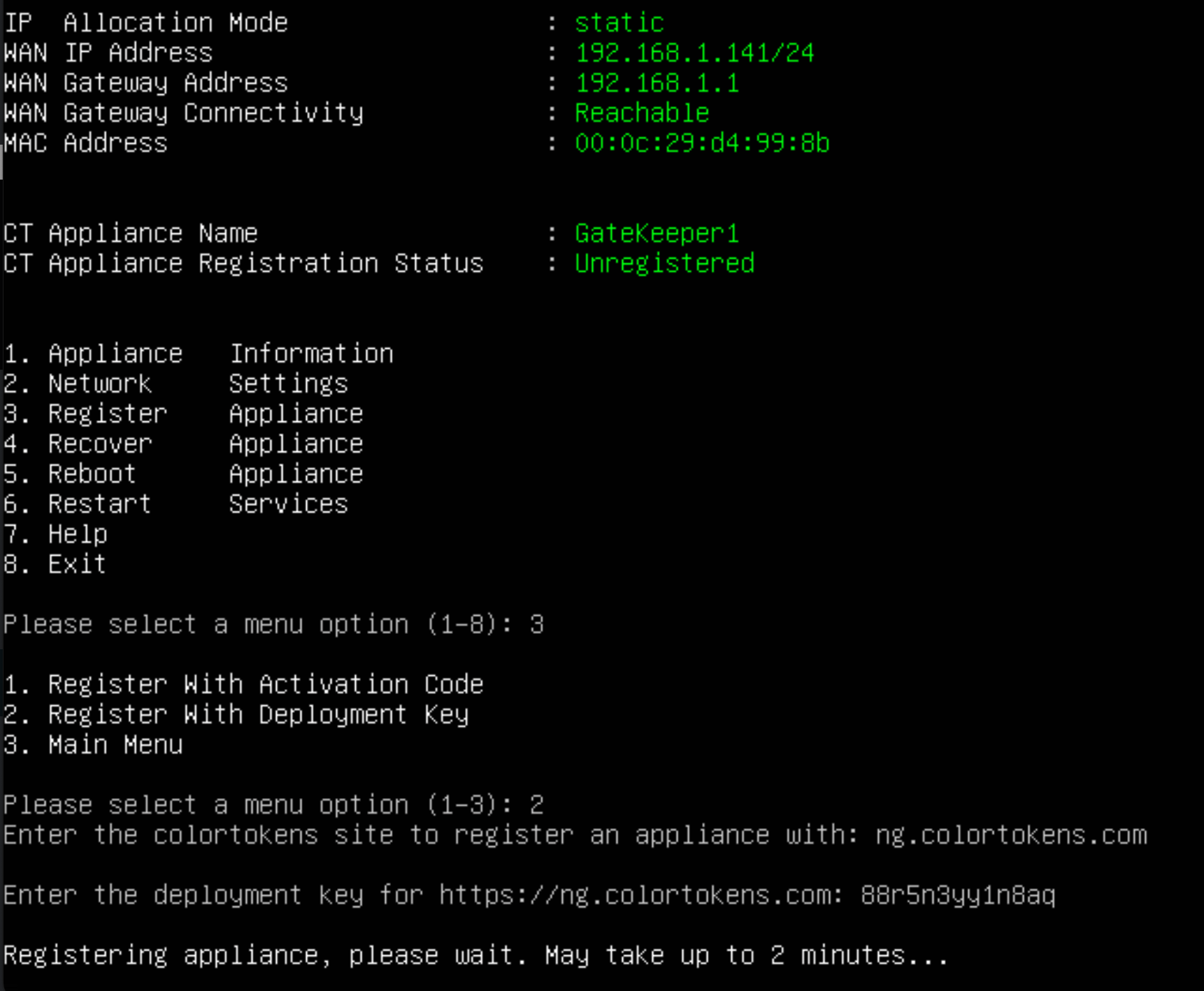
- Select Option 1 to Register Gatekeeper with Activation Code.
- Copy the activation code from the CLI (Selected text as in below image)

- Login to Cluster and select required tenant
- Go to Sensors and then select Gatekeepers Option (Bottom left corner of the page as shown in below image)
- Click on Activate button (Top Right corner of the Gatekeepers page as shown in below image), a new window will open up asking to ente the activation code.
- Provide copied activation code from Step 2 and click on activate button (Placed at right bottom corner of the new drawer opened after Step 5 shown in below image).
- We see gatekeeper name is detected and activation progress indication will be seen as shown in below image
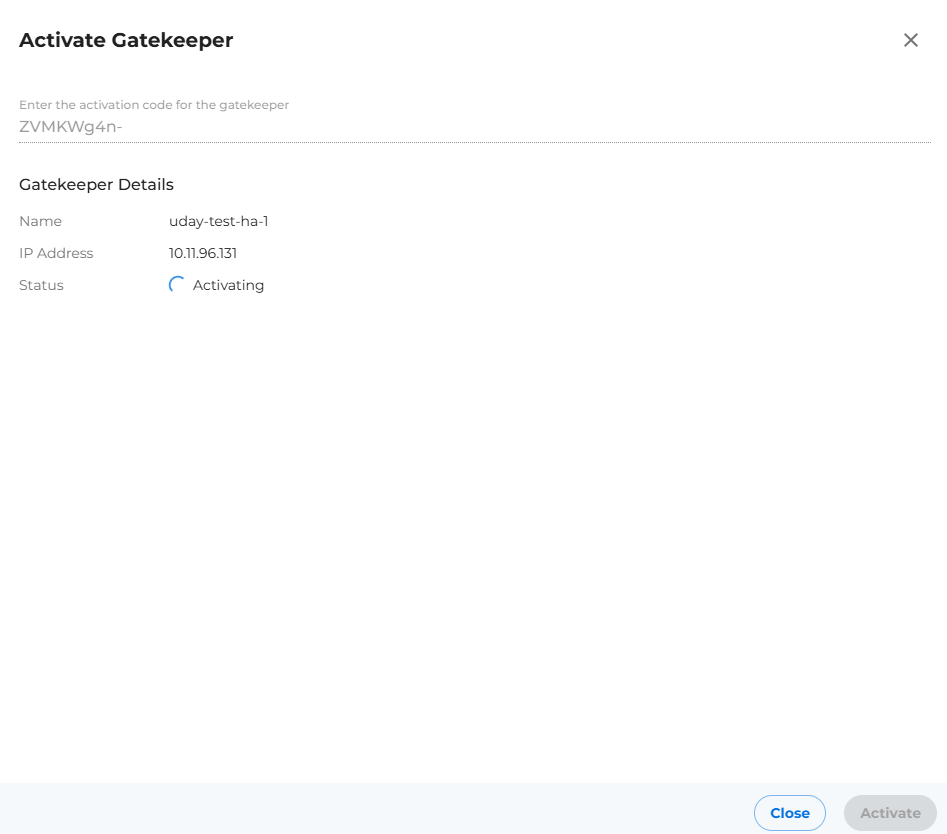
- Enter y as input in gatekeeper activation CLI as activation triggered from UI

- Wait for the activation to complete, Message will be shown in left bottom corner as shown in below image.
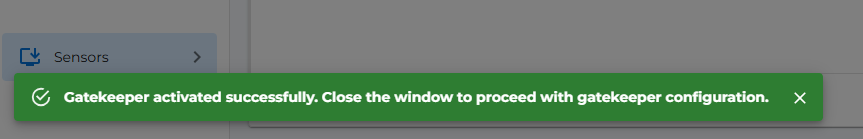
- Close the drawer and refresh the page to see the gatekeeper in the list. Go to gatekeeper options to configure the gatekeeper.
Method 2: Register with Deployment Key
- Copy the deployment key from Colortokens portal by clicking on [Gatekeeper (Left menu bar) --> Install Gatekeeper --> Register Instructions ] and paste it into the CLI.
- Initiate activation and wait for process to complete.
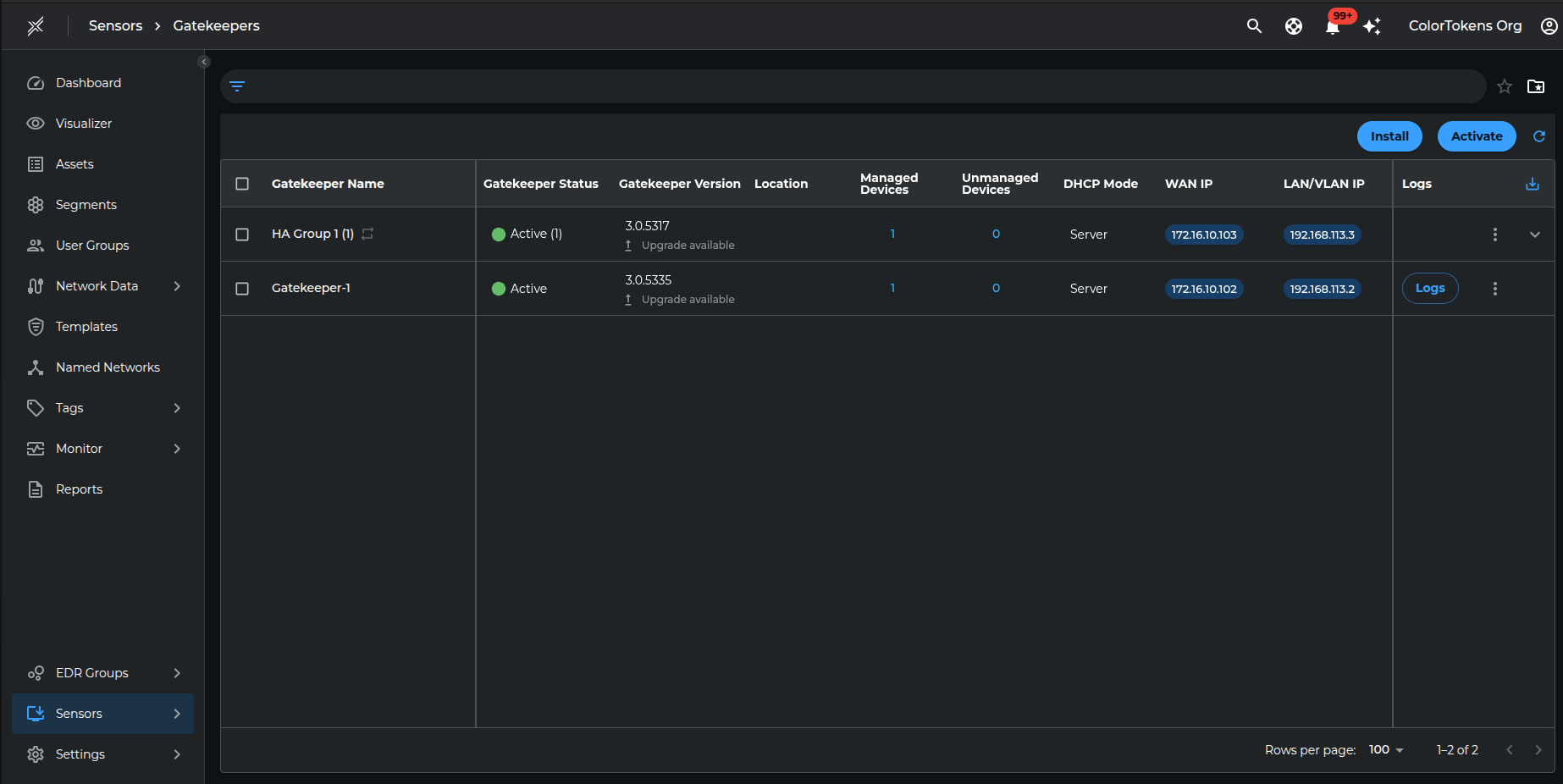
- Verify your gatekeeper is registered on the Gatekeeper List. If its ready, go ahead and configure the gatekeeper.
At this point the gatekeeper should be able to communicate to the Xshield console and should be visible on the platform, as shown in picture below:
Gatekeeper Configuration
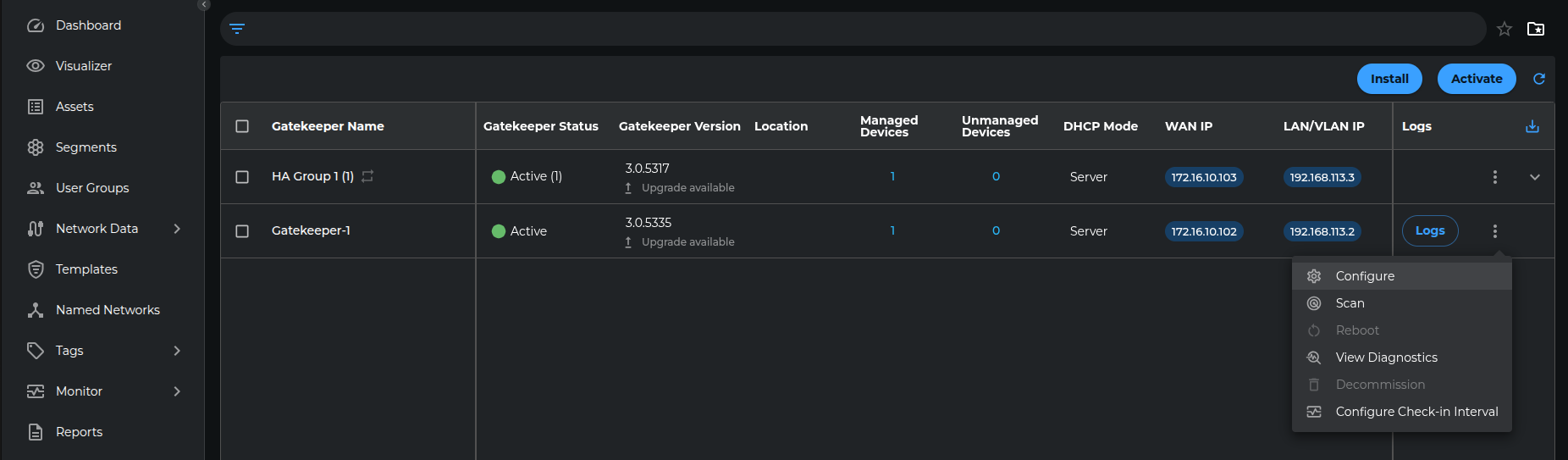
In Gatekeeper List, as shown in the above figure, configuration of the gatekeeper is conducted by clicking on the three dot icon (--> Configure button) located on the right side of the corresponding row. Selecting the configure button opens the gatekeeper configuration UI, allowing users to configure the gatekeeper directly from the console.
For detailed configuration instructions, interface setup, and advanced options, refer to the Gatekeeper Configuration UI documentation.
Gatekeeper Modes of Operation
The gatekeeper can be configured in two modes:
Standalone Mode
A single gatekeeper operates independently to secure the network segment.
High Availability (HA) Mode
Two or more gatekeepers work together in active/standby or active/active mode. When setting up an HA gatekeeper pair, each gatekeeper must be brought up (following the above steps) and configured individually through the configuration screen. For more details, refer to the High Availability documentation.
Network Addressing Modes
The gatekeeper supports following addressing modes for managed devices:
Static Mode
If using static mode, all static devices' network configuration will need to be modified to specify the gateway IP and netmask for the static device. Gateway IP should be set to the LAN Virtual IP of the gatekeeper. The netmask should be set to /32 or 255.255.255.255 in the devices network settings. This will ensure the static IoT / OT devices send all their traffic via the gatekeeper.
DHCP Mode
If using DHCP mode (relay/server), the routing of traffic via the gatekeeper is done automatically by the gatekeeper as part of the DHCP protocol. For DHCP devices, disconnect and connect back the devices so they can get a new DHCP lease from the gatekeeper if using DHCP server mode. If using DHCP relay mode, the device will automatically renew its address and should not need to be reconnected.
In the case of DHCP server / relay mode it is important to ensure that the Gatekeeper is the only DHCP relay / server in the entire subnet. DHCP is a broad cast protocol and it necessitates only one DHCP server / relay in a subnet.